 For industrial operations, dependable, high-quality power is necessary. An interruption in the power supply might halt production, resulting in expensive unplanned downtime. The majority of facilities use some type of commercial generator to reduce possible power supply concerns. Such a crucial piece of equipment must be well-maintained.
For industrial operations, dependable, high-quality power is necessary. An interruption in the power supply might halt production, resulting in expensive unplanned downtime. The majority of facilities use some type of commercial generator to reduce possible power supply concerns. Such a crucial piece of equipment must be well-maintained.
In the sections that follow, we go over the value of routine generator maintenance as well as the essential parts of generators and how they should be maintained. To help you get started creating schedules for your equipment, we have included a generator maintenance checklist that contains some general preventive maintenance guidelines. Your manufacturer and your specific facility will determine what unique checklists are needed based on their requirements.
Importance of Generator Maintenance
Generator maintenance is crucial to a system’s proper functioning and reduces the possibility of mishaps, minimizing accidents, and expensive repairs down the line. Regular maintenance also ensures that your generator will operate effectively and without interruption in the event of a power outage.
If you don’t maintain your generator, the system may begin to experience complications and damage that will affect the performance of the generator. Regular generator maintenance keeps an industrial generator functioning smoothly and guards against complications or system damage.
For each industrial generator, preventive maintenance is advised at least once a year. Two or even three preventative maintenance inspections may be required annually to guarantee the system’s safety and effectiveness, depending on the generator’s use and the surrounding conditions.
Types Of Industrial Generators
Industrial generators differ significantly from household versions. These generators must resist heavy use over an extended period of time in unfavorable circumstances. Industrial generators come in a variety of shapes and sizes, with outputs ranging from 150 hp to 4000 hp and sizes from 20 kW to 2500 kW. In order to acquire the best usage for your industrial purposes, you do need to choose the appropriate type.
Diesel Generators
Diesel engines are known for their longevity, reliability, and typically inexpensive maintenance requirements. Diesel engine’s endurance, toughness, and dependability are mostly due to the:
- The overall design of a diesel engine is gear-driven, with better lubrication, and less wear.
- The fuel used may cost slightly more, but tend to consume less fuel than gas generators, while performing the same work.
- A diesel engine is built with bigger and stronger components for heavy-duty performance.
- Diesel fuel burns more slowly than gasoline, which results in less heat and less engine wear.
- Due to diesel fuel’s higher energy density and increased efficiency, power generated by diesel generators can also be produced at a lower cost.
Disadvantages Of Using Diesel Generators
- Diesel units can be very noisy, so they’re often placed away from the work area.
- Another disadvantage of diesel generators is the production of hazardous exhausts such as carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxide, particulate matter, and others that are released into the atmosphere.
- When compared to other generator types, installing a diesel generator can be more expensive initially. However, compared to a gas-powered generator, you might discover that a diesel generator is more cost-effective over time because of how little it costs to operate and maintain it.
- Diesel is the least flammable of all generators or fuel sources.
Natural Gas Generators
Liquefied petroleum gas or propane are both used in natural gas generators. Natural gas has the benefit of being simple to store in underground or above-ground tanks. Additionally, it burns cleanly, which minimizes emissions-related issues. Natural gas-powered generators are dependable but can be more expensive when first purchased.
Disadvantages Of Using Natural Gas Generators
- The expense of installing gas lines makes natural gas installation more expensive.
- A natural gas line is highly explosive.
- Natural gas generators never have to be refilled.
- Technology companies make a great choice in natural gas generators as backup power sources.
Biodiesel
Biodiesel fuel is a blend of diesel and another biological source, like vegetable oil or animal fat Similar in both positives and negatives to regular diesel fuel, biodiesel has greater advantages for the environment. Biodiesel burns cleaner and produces fewer waste products while using fewer fossil fuels that aren’t renewable. Compared to normal diesel, this makes it a more environmentally responsible option. Compared to the other liquids and gases on this list, diesel fuels are all less flammable but noisy.
Portable Industrial Generators
Industrial portable generators are trailer-mounted models rather than the kind you can drag behind you as you walk. Large portable generators make an excellent choice for use on construction sites before an electrical supply is established. These are frequently used by emergency responders when a large amount of power is needed on location.
Disadvantages Of Using Natural Gas Generators
- The fumes that portable generators release are unhealthy for you. They must be located in a purpose-built space or outside to prevent the fumes from gathering. If you keep your generator indoors, it is a good idea to install a carbon monoxide detector.
- They offer a limited power supply, making them less suited for high-power demand.
- They are often stored for long periods of time and will require additional maintenance.
Propane
Propane-powered generators are very dependable. Even during a power outage, propane is easily accessible. Propane is easy to store and works well in cold environments. This means that a propane generator can dependably start up and produce power even if the power goes out on the coldest winter day.
Disadvantages Of Using Natural Gas Generators
- Propane burns faster than diesel generators, making them more costly to maintain.
- Propane is highly flammable.
Marine Generators
Marine generators of commercial or industrial grade are built to endure harsh environmental conditions. This type of generator is required for use near salt water and is recommended for large vessels or oil rigs. Diesel is the preferred fuel for industrial applications even though gas and diesel-powered marine generators are both available.
Heavy Fuel Oil Generators
Heavy fuel oil (HFO) is a petroleum distillate or hydrocarbon fuel, that is produced from crude oil, from which lighter hydrocarbon products like diesel and gasoline are also extracted. HFO or heavy fuel oil is the most widely used type of fuel for commercial vessels.
Generator Sizing
To pick the right generator size, you must take into account your overall power needs in kilowatts. The kind of equipment you’ll be using also affects the results. When starting up, equipment with motors or compressors uses more energy than when it is operating. If you don’t factor this into your overall needs, you could overload your generator. When choosing a generator there are many disadvantages to choosing a size too small.
Important Parts Of An Industrial Generator
Control Panel
The control panel for the generator consists of a number of parts that provide information and parameters like current, voltage, and frequency. Control panels typically feature switches or buttons to ensure the generator’s operation and are displayed on either built-in screens, gauges, or meters.
These control panels give users the ability to view system operations, diagnostics, and the status of the generator’s operator at any given time. Generators are large, bulky pieces of equipment that are vulnerable to overheating, wear and tear from continuous usage, speed changes, and engine stress. It’s crucial to keep an eye on the temperature of the coolant and oil, two crucial generator components.
Fuel System
Maintaining fuel flow to the engine is the responsibility of fuel systems. The type of fuel system depends on the type of fuel used by the engine of the generator.
Leaks and gasoline cut-off valve obstruction are the two most frequent issues with fuel systems. Due to the high combustibility of fuels, problems with fuel systems might become disastrous.
Alternator
It serves as the main part of commercial generators. This part is responsible for converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. The alternator has a stator, rotor, and brushes to carry the power generated. According to its specifications, the rotor must rotate at certain speeds. One of the main factors contributing to generator explosions is a very quick spin.
Alternator coils are prone to breaking and unwinding. The brushes, which are often comprised of carbon, are extremely brittle and prone to damage.
Engine
The engine burns fuel to provide mechanical energy that powers the alternator. Its features are similar to those of an internal combustion engine.
As the ratio of fuel to electricity declines due to poor engine performance, the generator’s performance will also decline.
Lubricant
Generators use lubricants frequently, just like any piece of machinery with moving parts. Regular lubrication of the alternator bearings and engine parts is necessary to lower friction.
After extended durations of operation, the lubricant is easily contaminated. To maintain the generator’s performance, they should be changed frequently.
Voltage Regulator
The alternating current comes from the generator. Depending on the alternator’s speed, the magnitude will change. The output voltages may change due to any alterations or glitches.
And now for the catch. Consistent voltage is required for industrial use to function normally. Regulating the electricity output from the generators is the responsibility of voltage regulators.
Skid
A generator’s primary base, often known as a skid, is where all of its parts are mounted. To make sure it is held firmly in place in an indoor generator room, the skid is frequently fixed to the floor. This skid acts as the main base of a generator set and offers a lot of flexibility aside from holding generator parts and components.
Regular maintenance is important for spotting minor problems in the earliest stages, stopping them from getting worse over time and damaging the generator, and giving you the chance to address them while they are more affordable and easier to fix. Without routine maintenance, you run the danger of needing more costly fixes as well as substantial, occasionally irreversible damage to the generator.
Cooling And Exhaust Systems
Fuel is burned by the engine to produce mechanical energy. The combustion waste must be effectively ejected by an exhaust system. After prolonged use, the alternator may become very hot due to various operational and environmental conditions.
Heat must be ventilated using a cooling system. The generator may shut down or result in other failures if these systems aren’t functioning properly.
Battery
Early generator models required a crank to turn them on. Fortunately, things have evolved.
A generator’s start-up function is now battery-powered. The generator generates power, which is used to recharge the battery. As a result, the generator cannot be started if the battery is not holding a charge.
Risks Of Delayed Maintenance
The optimum performance of your generator depends on routine preventative maintenance, which also minimizes risks like:
Lack of Power
Not being able to produce power efficiently is one of the most obvious problems an industrial generator may encounter. A generator may lose its effectiveness and overall energy capacity if it is ignored for a long time. An industrial generator needs routine maintenance to remain functional and provide power during a power failure.
Hazardous Situations
Without routine maintenance, an industrial generator may present safety issues including a carbon monoxide leak. Carbon monoxide, a colorless and odorless gas that poses significant safety dangers, is emitted as industrial generators operate. To guarantee you are alerted to any potential carbon monoxide emissions, you should maintain your generator as well as make sure your carbon monoxide detectors are in good working order.
If the generator is wet or is surrounded by a lot of moisture or water, it may also increase the danger of shock or electrocution accidents. To reduce risks, users of industrial generators in damp environments must make sure that the generator undergoes routine maintenance and is protected from contact with moisture.
Improperly storing fuel or gasoline that has spilled onto engine components raises the risk of fires and is another possible problem. Routine maintenance enables technicians to see any weak or compromised parts of a generator that could raise the risk of a fire or other accidents.
Expensive Repairs
Regular maintenance should never be put off because it can result in more costly repairs and problems. Avoiding routine maintenance does not save money; it leads to more expensive repairs that could have been minimized or avoided altogether.
Regular maintenance is crucial for spotting minor problems in the earliest stages, stopping them from getting worse over time and damaging the generator, and giving you the chance to address them while they are more affordable and easier to fix. Without routine maintenance, you run the danger of needing more costly fixes as well as substantial, occasionally irreversible damage to the generator.
Even though you may not need your generator’s power right now, neglecting to properly maintain it could significantly affect its functionality later on. You want to know that your generator will run properly and efficiently in the event of a power outage. Maintenance can ensure your generator provides safe, reliable, and predictable power during an outage.
Reasons Why Industrial Generators Need Maintenance
It’s important to plan routine inspections of an industrial generator, which should include fuel, oil, and coolant samples. Some reasons to complete generator maintenance include:
Keep Key Operations Running During Power Outages: Industrial generator maintenance helps keep a generator ready to run at a moment’s notice and provides a dependable source of power during a power outage.
Improve Efficiency: An industrial generator is more likely to operate smoothly and experience fewer unanticipated struggles if it is frequently inspected and maintained. As minor problems are promptly addressed with routine maintenance, generator owners can trust that their unit is finely tuned and dependable.
Lower Risk Of Accidents: Frequent maintenance can lower the risk of potential accidents or injuries. Accidents, including fires, carbon monoxide leaks, and other issues, are more likely to occur when systems are not properly maintained. Accident risk can be reduced by making sure there is adequate ventilation and a working generator.
Early Detection Of Problems Is Essential: Over the course of a generator’s lifespan, minor issues or complications should be anticipated. Preventive measures can help minimize the risk of these issues developing. Additionally, routine maintenance can spot a problem in the very early stages, enabling a more thorough tune-up and averting the need for more costly repairs down the line.
Ensure Important Systems Stay Operational: A generator offers a dependable backup power supply for essential equipment that must always be up and running. It is designed to keep critical systems operational.
Increase The Generator’s Lifespan: Diesel fuel generators are known for providing reliable, long-lasting options. Despite their durability, generators benefit from regular maintenance, which extends their lifespan. The system can be kept running well for the duration of its estimated lifespan with routine inspections and minor modifications, which can also prevent major problems in the future.
Manage Costs: Routine generator inspections and maintenance is a cost-effective strategy that can result in long-term cost savings. The cost of routine maintenance vastly outweighs the expenses associated with letting your generator go without inspection. The longer you go without routine inspections, the more expensive repairs tend to be.
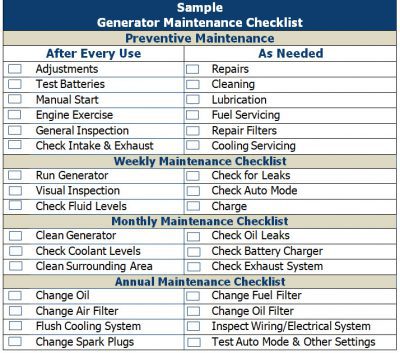
Industrial Generator Maintenance Checklists
A gas or diesel generator is not the kind of equipment you can set up and forget about. Before each use, the generator should be visually inspected, and a maintenance program with weekly, monthly, and yearly reviews should be made.
A regular maintenance schedule is crucial to avoid breakdowns and prolong the life of your gas or diesel generator.
A generator maintenance checklist helps you prioritize which parts to check and when to check them, so you can keep the generator running properly when you need it most.
Note: These are general preventive maintenance guidelines. Your manufacturer and your specific facility will determine what unique checklists are needed based on their requirements.
Final Thoughts
When the main power supply fails, industrial facilities should have a generator as backup power. It’s essential to keep the generator operating at peak performance. Often, it is overlooked as generators are rarely used. Generator maintenance must be taken seriously in order to avoid major catastrophes due to a generator failing.
Because there are so many moving parts in generators, each one needs to be inspected frequently. A maintenance schedule for generators should be developed using input from OEMs, maintenance teams, and operating data. For maintenance procedures, create checklists and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs).
In managing all of these tasks, along with the resources, inventory, and preventive maintenance schedules, you need a compressive tool to help keep everyone on schedule and get these tasks done. Investing in a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) will help you manage all of these tasks and resources within one centralized system.
